Blog
The latest nanoparticle articles from Nikalyte Ltd.
Thin Film Lithium Niobate Deposition via Magnetron Sputtering
Thin Film Lithium Niobate (TFLN) has become one of the most sought-after materials in modern photonics and integrated optoelectronics. With applications in telecommunications, quantum computing, photonic integrated circuits (PICs), and high-frequency electro‑optic modulators, TFLN is increasingly recognised as a cornerstone material for next‑generation optical technologies. [1],[2] Among available physical vapour deposition (PVD) techniques, magnetron sputtering

Detecting Forever Chemicals in our waterways with SERS
The global water quality crisis extends across continents, with the United Kingdom facing significant contamination challenges from Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), commonly known as forever chemicals. These synthetic compounds persist in the environment for decades, accumulating in our bodies and waterways. As regulatory agencies establish stricter drinking water standards, the need for rapid, accurate

The Role of SERS in detecting Nitazene
The opioid crisis has entered a dangerous new phase. While fentanyl continues to dominate headlines, an even more potent class of synthetic opioids has emerged from the shadows, nitazenes. These 2-benzylbenzimidazole compounds, originally synthesized in the 1950s but abandoned due to extreme toxicity, have resurfaced on illicit drug markets with devastating consequences.[1] Traditional laboratory analysis

Silver nanoparticle coatings for wound dressing applications
In the evolving field of advanced wound care, silver nanoparticle (AgNP) coatings have become a cornerstone for developing antimicrobial dressings that are both effective and biocompatible. Among various fabrication techniques, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) stands out for its ability to deliver precise, reproducible, and scalable silver coatings at the nanoscale. This blog explores how PVD
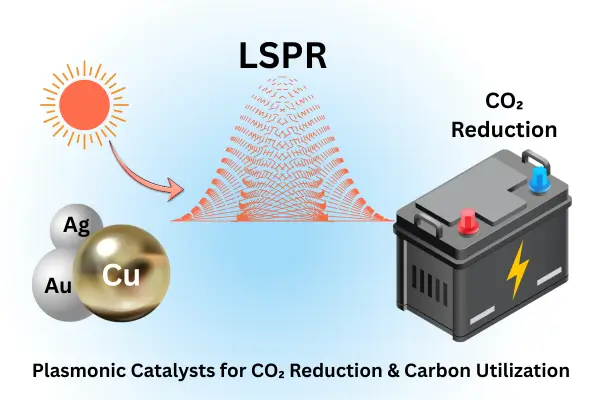
Plasmonic Catalysts for CO₂ Reduction & Carbon Utilization
The global push towards carbon neutrality has accelerated research into advanced catalytic systems that can convert CO₂ into valuable fuels and chemicals. Among the many emerging strategies, plasmonic catalysts for photo-thermal CO₂ reduction are gaining significant attention from researchers, students, professors, and industry experts alike. This article explores the fundamentals, mechanisms, and recent breakthroughs in

Why is Niobium Critical for Quantum Materials
The field of quantum materials has seen tremendous growth, especially in quantum computing, photonics, and optoelectronics. Among the most promising materials are doped II-VI nanocrystals, which possess unique electronic and optical properties that are highly sought after for next-generation technologies. These materials are engineered at the atomic scale to control their electrical and optical behaviour,
Doped II-VI Nanocrystals for Quantum Materials
The field of quantum materials has seen tremendous growth, especially in quantum computing, photonics, and optoelectronics. Among the most promising materials are doped II-VI nanocrystals, which possess unique electronic and optical properties that are highly sought after for next-generation technologies. These materials are engineered at the atomic scale to control their electrical and optical behaviour,

Hybrid MBE Source for Advanced Battery Electrode Deposition
As the demand for advanced energy storage systems continues to soar, researchers and engineers are increasingly turning to cutting-edge deposition technologies to optimize battery performance. One such innovation is the Hybrid Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) Source for advanced battery electrode deposition. This hybrid approach is a game-changer for the design, fabrication, and enhancement of electrode
High-Temperature Superconductors Shaping the Future of Quantum Materials
Imagine a world where electricity flows without resistance, powering everything from quantum computers to futuristic transportation systems. High-temperature superconductors (HTS) are making this vision a reality, and they’re set to change the game in ways we never thought possible! By enabling electricity to flow without resistance at higher temperatures than traditional superconductors, HTS are transforming
Plasmonic Interactions in Quantum Sensing Materials
Plasmonics, the study of light interacting with free electrons on metal surfaces, has become an essential tool for advancing quantum technologies. By exploiting the unique properties of plasmonic materials, typically metals such as gold, silver, and copper, researchers have opened new avenues for improving the sensitivity, precision, and capabilities of quantum systems. In particular, the

SERS for Biosensing Applications
Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) has rapidly gained recognition as a groundbreaking biosensing technique, enabling the accurate, rapid, and non-invasive detection of diseases, pathogens, and environmental toxins. By significantly amplifying Raman signals through nanomaterials, SERS makes it possible to detect trace amounts of biological analytes, positioning it as a leading method for medical diagnostics, food safety,

What is Electron Beam Evaporation?
Electron Beam Evaporation (E-Beam Evaporation) is a precise Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process used for applying high-density, thin coatings to substrates. E-Beam Evaporation operates under high vacuum conditions and employs a focused electron beam to evaporate the coating material (source material), which is then deposited onto a substrate.[1] This deposition method is essential for industries
